Manufacturing Process Of Wire Harnesses
- Share
- publisher
- John
- Issue Time
- Feb 19,2025
Summary
Wire harnesses—bundles of wires, terminals, and connectors—are the nervous system of modern machinery.
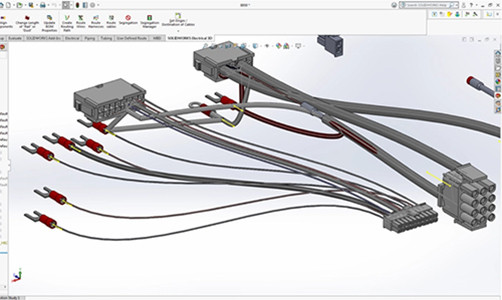
Executive Summary
The Manufacturing Process Of Wire Harnesses involves a series of precision steps—from design and material selection through assembly, testing, and delivery—that ensure reliable, high‑performance electrical interconnect solutions for industrial and automotive applications. B2B buyers care most about customization capabilities, on‑time delivery, rigorous quality controls, and long‑term cost savings. Leveraging ISO‑certified facilities, advanced automation equipment, and end‑to‑end supply‑chain integration, our company delivers tailor‑made wire harness solutions that reduce installation time, improve system reliability, and drive measurable ROI.
1. Introduction to Wire Harness Manufacturing
Wire harnesses—bundles of wires, terminals, and connectors—are the nervous system of modern machinery. From solar inverters and robotic arms to heavy‑duty vehicles and medical devices, they carry critical power and signals. Understanding the Manufacturing Process Of Wire Harnesses is key for OEMs and system integrators seeking partners that can deliver flawless, cost‑effective assemblies at scale.

2. Key Phases in the Manufacturing Process Of Wire Harnesses
2.1. Design & Engineering
Requirements Gathering: Define electrical, environmental, and mechanical specs.
3D Modeling & Prototyping: CAD tools simulate routing and strain relief.
DFM Reviews: Design‑for‑manufacturing checks to minimize errors and cost.

2.2. Material Selection
Conductor Choice: Copper, tinned copper or aluminum, based on conductivity and flex life.
Insulation & Jacketing: PVC, TPE, silicone, or cross‑linked polyethylene to meet temperature and chemical resistance.
Connector & Terminal Sourcing: Overmolded or free‑hanging, from standard M8/M12/M16/7-8 up to custom automotive‑grade housings.

2.3. Cutting & Stripping
Automated Cutting Machines: Laser‑guided precision to within ±0.1 mm.
Robotic Wire Strippers: Consistent strip lengths for reliable crimp quality.

2.4. Crimping & Soldering
High‑Force Crimp Presses: ISO‑certified tooling ensures each crimp meets electrical and mechanical pull‑out requirements.
Selective Soldering: Automated wave or dip soldering for complex PCBA‑integrated harnesses.

2.5. Assembly & Routing
Harness Boards & Fixtures: Custom jigs hold wires in precise configurations for bundling.
Binding & Overmolding: Heat‑shrink tubing, spiral wrap, or two‑component overmolds for strain relief, sealing, and aesthetics.
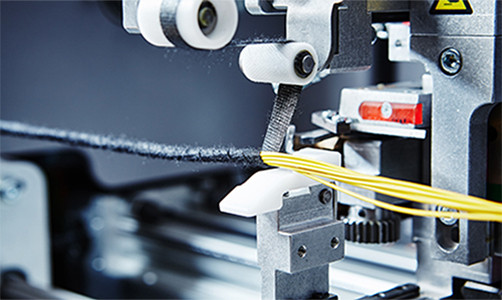
Pre-assembly process
The pre-assembly process aims to improve the efficiency of the final assembly, which is particularly important in the manufacture of complex wiring harnesses. To this end, a detailed pre-assembly process operating manual must be prepared.
In the pre-assembly process, the following aspects need to be noted:
Path planning: Reasonably arrange the assembly path of the wires to avoid cross interference.
Component identification: Assign a unique number to each component and affix it to the material box for easy identification and management.
On-site optimization: Technical personnel should regularly summarize on-site and continuously optimize the pre-assembly process to ensure that it adapts to actual production needs.
Assembly process
The assembly process is the last step in harness manufacturing and the most complicated link. According to the assembly tray designed by the product development department, design appropriate assembly equipment and material box specifications and dimensions. All assembly kits and accessories should be clearly numbered and affixed to the material box to improve assembly efficiency.
In the assembly process, the following points should be noted:
Connector installation: Ensure that the connector is correctly installed in the specified position, check whether the locking mechanism of the connector is in place to prevent loosening or falling off.
Waterproof performance: For connectors that need to be waterproof, ensure that the sealing ring is correctly installed and conduct waterproof tests to ensure that its waterproof level meets the design requirements.
Electrical test: After assembly, a comprehensive electrical test is required, including continuity, insulation resistance and hi-pot test, to ensure that the electrical performance of the harness meets the design requirements.
2.6. Testing & Quality Assurance
Continuity & Hi‑Pot Testing: 100% electrical verification under load.
Environmental Stress Testing: Vibration, thermal cycling, and salt‑spray chambers simulate field conditions.
Traceability & Documentation: Full batch records, certificates of compliance (RoHS, REACH), and detailed inspection reports.
Quality Control
Throughout the entire harness manufacturing process, quality control is carried out throughout. Effective quality control measures can ensure that the product quality of each link meets the standards, thereby improving overall production efficiency and product quality. Specific measures include:
Raw material inspection: Ensure that the wires, terminals and other materials used meet the design requirements.
Process monitoring: Real-time monitoring of the production process through online testing equipment to promptly detect and correct quality problems.
Finished product testing: Comprehensive functional testing of finished harnesses to ensure that their electrical and mechanical properties meet the standards.
3. Why B2B Customers Choose Us
3.1. End‑to‑End Supply‑Chain Integration
Our vertically integrated operations—from precision metal stamping and injection molding to automated assembly lines—eliminate middlemen, reduce lead times, and control costs.
3.2. Advanced Automation & Capacity
Equipped with Swiss Charmilles EDM, Japanese Sodick wire‑cutting, and over 100 automatic assembly machines, we scale rapidly for both prototype runs and high‑volume production.
3.3. Certified Quality & Compliance
ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 certified, all products meet RoHS and REACH standards.
3.4. Customization & Agile Engineering
Dedicated R&D team works closely with clients to develop specialized connectors, bespoke overmolding compounds, and tailored harness layouts that optimize installation and maintenance.
4. Customer Pain Points & Our Solutions
| Pain Point | Our Solution |
| Long lead times | Flexible shift schedules and buffer inventory enable 2–4 week standard lead. |
Quality inconsistency | 100% in‑line testing and SPC data analytics eliminate batch variation. |
Hidden costs & overruns | Transparent quoting system and lean manufacturing drive cost predictability. |
Lack of technical collaboration | Dedicated application engineers provide DFMEA and on‑site support. |
Complex compliance requirements | We maintain full certification library and advise on evolving regulations. |
5. Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the typical lead time for a custom wire harness order?
Standard lead time for prototypes is 2–3 weeks; full production runs typically ship within 4–6 weeks, depending on complexity and volume.
Q2: Can you handle small‑batch or low‑volume runs?
Yes. Our modular assembly cells allow economical production runs from 10 to 10,000 units without significant setup charges.
Q3: How do you ensure electrical reliability?
Every harness undergoes 100% continuity and hi‑pot testing, plus sample pull tests and environmental stress screening before shipment.
Q4: Do you provide UL, CE ?
We offer UL‑approved cables, CE verification.
Q5: What customization options are available?
From conductor gauges and insulation compounds to overmolding shapes, connector brands, and full kitting, we tailor every attribute to your application.
6. Development Trends
With the advancement of technology, the manufacturing process of wire harnesses is also constantly developing. In the future, wire harness manufacturing will be more automated and intelligent to cope with increasingly complex market demands. For example, automated production lines can significantly improve production efficiency and reduce human errors; while intelligent management systems can help companies better manage production and quality.
With the rapid development of new energy vehicles, smart devices and other fields, wire harness manufacturing also needs to face new challenges such as high voltage, high speed and lightweight. This requires manufacturers to continuously develop new materials and technologies to meet market demand.
The wire harness manufacturing process is a complex process involving multiple links, from stripping to crimping, to pre-installation and final assembly, each step requires strict quality control and technical support. By continuously optimizing the process flow and adopting advanced technology and equipment, the high performance and high reliability of wire harness products can be ensured to meet the growing needs of different industries. With the continuous development of technology, the future wire harness manufacturing process will be more automated and intelligent, bringing more efficient and reliable solutions to all walks of life.